Page 37 - NovDefComp
P. 37
Scorecard System Methodology™
Asset Allocation Strategies
Asset allocation strategies are investment strategies that invest in a broad array of asset classes that may include U.S. equity, international equity,
emerging markets, real estate, fixed income, high yield bonds and cash (to name a few asset classes). These strategies are typically structured in
either a risk-based format (the strategies are managed to a level of risk, e.g., conservative or aggressive) or, in an age-based format (these strategies
are managed to a retirement date or life expectancy date, typically growing more conservative as that date is approached). For this type of investment
strategy, the Scorecard System is focused on how well these managers can add value, with asset allocation being the primary driver of investment
returns and the resulting Score. Multisector Bond (MSB) asset class follows the same evaluation criteria with some slightly different tolerance levels
where noted. These managers are also evaluated on both their asset allocation and security selection.
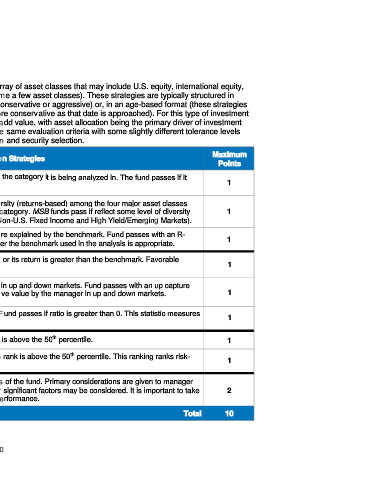
Maximum
Weightings Asset Allocation Strategies
Points
Risk Level: The fund’s standard deviation is measured against the category it is being analyzed in. The fund passes if it
falls within the range for that category. 1
Style Factors Style Diversity: Fund passes if it reflects appropriate style diversity (returns-based) among the four major asset classes
30% (Cash, Fixed Income, U.S. & International Equity) for the given category. MSB funds pass if reflect some level of diversity 1
among fixed income asset classes (Cash, U.S. Fixed Income, Non-U.S. Fixed Income and High Yield/Emerging Markets).
R-Squared: Measures the percentage of a fund’s returns that are explained by the benchmark. Fund passes with an R- 1
squared greater than 90 percent. This statistic measures whether the benchmark used in the analysis is appropriate.
Risk/Return: Fund passes if its risk is less than the benchmark or its return is greater than the benchmark. Favorable
risk/return characteristics are desired. 1
Risk/Return Up/Down Capture Analysis: Measures the behavior of a fund in up and down markets. Fund passes with an up capture
Factors greater than its down capture. This analysis measures the relative value by the manager in up and down markets. 1
30%
Information Ratio: Measures a fund’s relative risk and return. Fund passes if ratio is greater than 0. This statistic measures 1
the value added above the benchmark, adjusted for risk.
th
Returns Peer Group Ranking: Fund passes if its median rank is above the 50 percentile. 1
Peer Group
Rankings Sharpe Ratio Peer Group Ranking: Fund passes if its median rank is above the 50 percentile. This ranking ranks risk-
th
20% 1
adjusted excess return.
Qualitative Two points may be awarded based on qualitative characteristics of the fund. Primary considerations are given to manager
Factors tenure, fund expenses and strength of statistics, however, other significant factors may be considered. It is important to take 2
20% into account nonquantitative factors, which may impact future performance.
Total 10
10